Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Portuguese Journal of Public Health
Print version ISSN 2504-3137On-line version ISSN 2504-3145
Port J Public Health vol.36 no.3 Lisboa 2018
https://doi.org/10.1159/000493987
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Adolescents from 1988 to 2014: Results from the HBSC Portuguese Survey
Prevalência de excesso de peso e obesidade dos adolescentes portugueses de 1988 a 2014: Resultados do HBSC
Adilson Marquesabc Margarida Gaspar de Matos cd Maria do Céu Machado e Ana Naia df Jorge Motag
aCentro Interdisciplinar de Estudo da Performance Humana, Faculdade de Motricidade Humana, Universidade de Lisboa, Cruz Quebrada, Portugal
bCentro de Investigação em Saúde Pública, Escola Nacional de Saúde Pública, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
cInstituto de Saúde Ambiental, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
dFaculdade de Motricidade Humana, Universidade de Lisboa, Cruz Quebrada, Portugal
eFaculdade de Medicina, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
fCentro de Investigação em Arquitetura, Urbanismo e Design, Faculdade de Arquitetura, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
gCentro de Investigação em Atividade Física Saúde e Lazer, Faculdade de Desporto, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal
ABSTRACT
Objective: Using a national representative sample of Portuguese adolescents, this study aimed to report the prevalence of overweight and obesity over 16 years, from 1998 to 2014. Methods: The total sample comprised 26,479 adolescents (12,711 boys and 13,768 girls) aged 11-16 years (mean age ± SD = 13.5 ± 1.7) from the Health Behaviour in Schoolaged Children (HBSC) Portuguese survey cohorts from 1998 (n = 5,999), 2002 (n = 5,454), 2006 (n = 4,430), 2010 (n = 4,702), and 2014 (n = 5,894). Weight and height were selfreported. The prevalence of overweight and obesity was calculated along with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: The highest prevalence of overweight and obesity was achieved in 2010 (20.5%; 95% CI: 19.5, 21.9) and the lowest in 1998 (17.8%; 95% CI: 16.8, 18.8). The results of trend tests between 1998 and 2014 show that there was no significant change in overweight and obesity prevalence. Although the prevalence of obesity increased from 1998 to 2014 for the entire sample (0.8%; 95% CI: -5.5, 7.0), for boys (1.1%; 95% CI: -4.1, 6.3), and girls (0.5%; 95% CI: -4.5, 5.4), there were no significant changes in obesity prevalence. Conclusion: The prevalence of overweight and obesity in Portuguese adolescents was around 20% between 1998 and 2014. The extent of overweight and obesity seems to have stabilized over time.
Keywords: Excess weight · Children · School · HBSC
RESUMO
Objetivo: Com uma amostra representativa de adolescentes portugueses, o objetivo do estudo foi reportar a prevalência de excesso de peso e obesidade entre 1998 e 2014. Metodologia: Participaram no estudo 26,479 adolescentes (12,711 rapazes, 13,768 raparigas) com idades entre os 11 e os 16 anos (M = 13.5 ± 1.7), que participaram no estudo Health Behaviour in Schoolaged Children (HBSC) em 1998 (n = 5,999), 2002 (n = 5,454), 2006 (n = 4,430), 2010 (n = 4,702), e 2014 (n = 5,894). O peso e a altura foram auto reportados. A prevalência de excesso de peso e obesidade foi calculada para um intervalo de confiança de 95%. Resultados: O valor mais elevado para a prevalência de excesso de peso e obesidade foi observado em 2010 (20.5%, 95% CI: 19.5%, 21.9%) e o valor mais baixo foi registado em 1998 (17.8%, 95% CI: 16.8%, 18.8%). Os resultados da tendência entre 1998 e 2014 mostram que não houve mudanças estatisticamente significativas na prevalência de excesso de peso e obesidade. Relativamente aos valores da obesidade, apesar de se verificar um aumento entre 1998 e 2014 para a globalidade da amostra (0.8%, 95% CI: -5.5%, 7.0%), para os rapazes (1.1%, 95% CI: -4.1%, 6.3%), e raparigas (0.5%, 95% CI: -4.5%, 5.45), não se verificou uma mudança estatisticamente significativa. Conclusões: A prevalência de excesso de peso e obesidade dos adolescentes portugueses rondou os 20% entre 1998 e 2014. Ao longo dos 16 anos os valores de prevalência de excesso de peso e obesidade estiveram estabilizados.
Palavras Chave: Excesso de peso · Crianças · Escola · HBSC
INTRODUCTION
Over the past 3 decades, the prevalence of adolescent obesity had increased worldwide, and due to serious public health consequences, it was considered a global epidemic 1. Indeed adolescent obesity increases the risk of experiencing a host of adverse health problems, such as metabolic syndrome, obstructive sleep apnea, dyslipidemia diabetes type II, hypertension 2, and a greater risk of bullying and social isolation 3. Moreover, overweight and obesity in adolescence tends to track into adulthood and becomes difficult to treat 4.
Therefore, collecting epidemiological data of obesity is important to support the development of preventive programs and public strategies 5. Using a national representative sample of Portuguese adolescents, this study aimed to report the prevalence of overweight and obesity over 16 years, from 1998 to 2014. Considering the national implemented policies for preventing overweight and obesity in schools and municipalities, we also wanted to evaluate if overweight and obesity in children is increasing.
METHODS
Participants and Procedures
The total sample comprised 26,479 adolescents (12,711 boys and 13,768 girls) aged 11-16 years (mean age ± SD = 13.5 ± 1.7) from the Health Behaviour in Schoolaged Children (HBSC) Portuguese survey cohorts from 1998 (n = 5,999), 2002 (n = 5,454), 2006 (n = 4,430), 2010 (n = 4,702), and 2014 (n = 5,894). The HBSC is an international survey that collects data on the health and wellbeing, social environments, and health behaviors of children and adolescents every 4 years. These data are used to gain new insight into young people’s health and wellbeing, to understand the social and psychological determinants of health, and to incorporate policies to improve young people’s lives. The methodological aspects of the HBSC study are well developed and published elsewhere 6. Briefly, the survey is based on a selfadministered questionnaire that is completed in public schools. The schools are randomly selected from a national list of schools, which has been stratified by Portuguese administrative regions. In each school, classes are randomly selected according to the number of students required for each grade. This research was in accordance with the Ethical Committee of Porto Medical School and the National Data Protection System. All school administrators gave their consent, the legal guardians gave written informed consent, and the students provided assent.
BMI
Weight and height were selfreported. The adolescents were aware of their weight and height because they performed a physical fitness test (FitnessGram) several times a year, and physical education teachers provided information about their weight and height. It should be noted that FitnessGram began to be widely used in schools in 2005. However, physical education teachers assessed students’ physical fitness with the Eurofit test battery, and many weighed and measured the height of their students.
Selfreporting weight and height is considered a valid tool for BMI estimates of overweight and obesity in epidemiological studies 7. BMI was then calculated, and the adolescents were classified into underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese categories according to age and genderspecific cutoff points proposed by the International Obesity Task Force 8. The cutoff points for adolescent overweight and obesity are linked to the widely accepted adult cutoff points of a BMI of 25 and 30. Because the number of underweight adolescents was very small, underweight and normal weight categories were defined as normal weight.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive data are presented as percentages, means, and standard deviation for each year’s survey. The differences between participants’ characteristics over time were tested by χ2 and ANOVA, for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. The prevalence of overweight and obesity was calculated along with a 95% confidence interval (CI). A p value < 0.05 was regarded as significant. Data analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 24.
RESULTS
Table 1 shows the characteristics of adolescents over time. There is a statistically significant difference between the BMI category and year’s survey for the total sample (χ2(12) = 45.201, p < 0.001), boys and girls (χ2(12) = 22.479, p = 0.032), and girls (χ2(12) = 37.246, p < 0.001). However, there is no possibility of establishing a pattern.
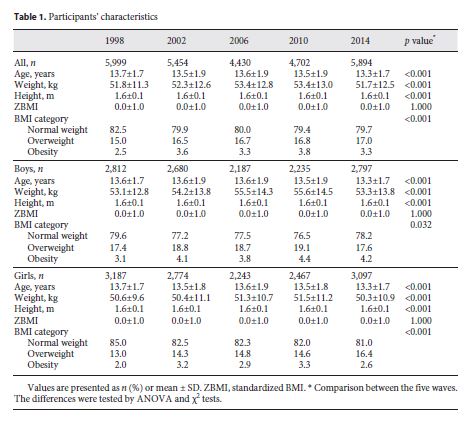
The prevalence of overweight and obesity by age and sex are shown in Table 2. Adolescents aged 11 years had the highest prevalence of overweight and obesity and, on the other hand, the oldest had the lowest prevalence. For the entire sample, the highest prevalence was achieved in 2010 (20.5%; 95% CI: 19.5, 21.9) and the lowest was in 1998 (17.8%; 95% CI: 16.8, 18.8). Of the boys, 23.7% (95% CI: 21.9, 25.5) were overweight or obese in 2010, and 19.1% (95% CI: 17.7%, 20.5%) of the girls in 2014. The results of trend tests between 1998 and 2014 show that there was not significant change in overweight and obesity prevalence.
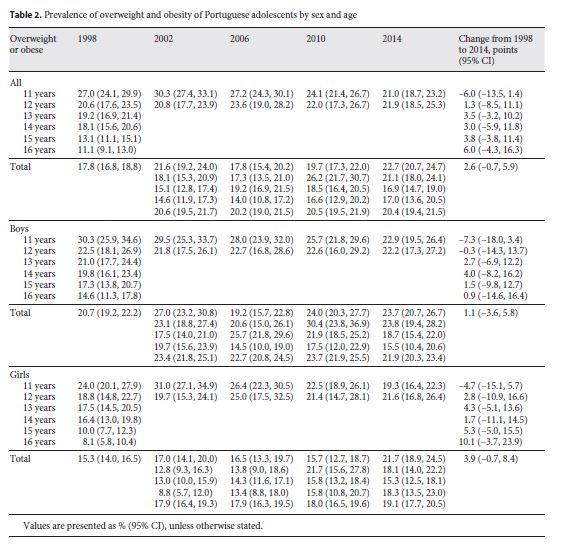
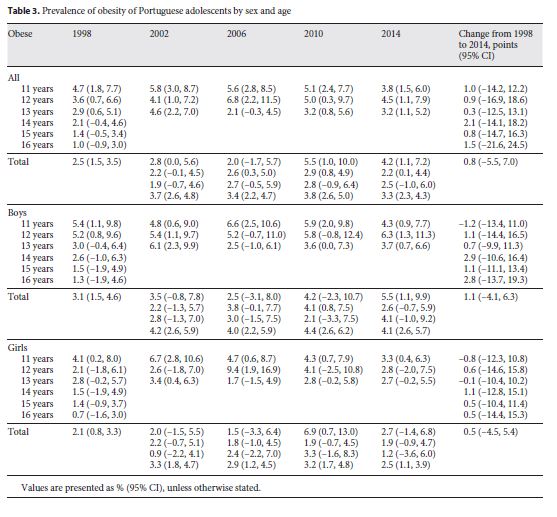
For the prevalence of obesity, the youngest (aged 11 and 12 years) presented the highest prevalence in all years surveys (Table 3). Among boys, the estimated prevalence of obesity was highest in 2010 (4.4%; 95% CI: 2.6, 6.2) and lowest in 1998 (3.1%; 95% CI: 1.5, 4.6). The highest prevalence among girls was in 2002 (3.3%; 95% CI: 1.8, 4.7) and the lowest was in 1998 (2.1%; 95% CI: 0.8, 3.3). Although the prevalence increased from 1998 to 2014 for the entire sample (0.8%; 95% CI: -5.5, 7.0), for boys (1.1%; 95% CI: 4.1, 6.3), and girls (0.5%; 95% CI: 4.5, 5.4), there were no significant changes in obesity prevalence.
DISCUSSION
This study aimed to report the prevalence of overweight and obesity of Portuguese adolescents over a period of 16 years, from 1998 to 2014. Trends and correlates of overweight and obesity among Portuguese adolescents from 2002 to 2010 were previously addressed in a different paper using data from the HBSC survey in Portugal 9. This study further expanded this information, adding data of 1998 and 2014, which is the most recent HBSC survey 10. The results of trend tests show that there was no significant change in overweight and obesity prevalence between 1998 and 2014.
The results from this study estimate that at least 1 in 5 adolescents is overweight or obese. This prevalence, which has been relatively stable over the years 11, is considered high as it was above the average of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development countries 12. These data are relatively consistent with the data from a previous crosssectional study in Portuguese youth, which also used a representative sample of children and adolescents 13. Furthermore, the study results are also in line with the results of the most recent data of childhood obesity surveillance in Portugal, with children aged between 6 and 8 years 14. There is a trend towards stabilization of the prevalence of overweight and obesity in children over the years. The results of this childhood obesity survey in Portugal are still similar in relation to the tendency to reduce the prevalence of obesity with increasing age. Analyzing the results together, the stability of the prevalence of overweight and obesity has occurred in childhood and adolescence.
Even though the prevalence of overweight and obesity is increasing in some parts of the world (15 ,16 , 17 ), in other parts, a levelling off of overweight and obesity among adolescents can be seen, such as in Australia, Japan, Russia, the United States, and some European countries (18 , 20 , 21 ). The results from the present study including Portuguese adolescents from 1998 to 2014 contributed to the growing evidence of the observed stabilization of the prevalence of overweight and obesity, refuting what has been suggested, namely that adolescent overweight and obesity are increasing exponentially. Since only recent studies have approached the levelling off in overweight and obesity, the reasons for stagnation in some countries are yet unclear. One reason could be that being overweight has been recognized as a public health concern, which has led to the implementation of programs to promote physical activity and healthy eating habits, mainly in the school setting to reach all children and adolescents. Another reason could be that children and adolescents with a predisposition to becoming overweight or obese have already become overweight or obese, and thus a saturation equilibrium was achieved 19. However, this theoretical explanation can easily be refuted because stabilization has been occurring at very different levels in different countries.
As observed previously in Portugal 13 and Spain 22, the prevalence of overweight and obesity is higher among the youngest adolescents. On the contrary, older adolescents in the United Stated of America were more likely to be overweight or obese (23 , 24 ). The differences may reflect sociocultural dissimilarities among countries and denote that the relationship between obesity and age is not determined biologically.
Some limitations and strengths should be addressed. First, height and weight were selfreported and are subject to bias. Nevertheless, selfreporting weight and height is considered a valid tool for BMI estimates in epidemiological studies 7, and BMI has been shown to correlate highly with dual energy Xray absorptiometry of body fatness in adolescents 25. Second, BMI does not discriminate between lean and fat mass. Yet, it is an appropriate measurement for the indirect assessment of adiposity in young people 26. Third, in studies that use data from samples from different periods of time, selfreporting weight and height might be subject to temporal changes because attitudes about overweight and obesity are changing 27. Although the present study used a representative sample of Portuguese adolescents, stratified by region, the analysis did not take into account socioeconomic data. This, perhaps, would be of importance because in Portugal, the socioeconomic status is a determinant of overweight and obesity among girls 28. The strengths of this study include the sample size, national representativeness in all years surveys, and the use of an international definition for overweight and obese status that allows a comparison between the year’s survey.
CONCLUSION
The prevalence of overweight and obesity in Portuguese adolescents was around 20% between 1998 and 2014. Despite the study’s methodological limitations, the extent of overweight and obesity seems to have stabilized over time. Nonetheless, the prevalence is still considered high, which means that a high proportion of adolescents may have the risk of a cardiovascular disease associated with excess weight. Therefore, strategies that promote healthy weight among children and adolescents, using families as partners, are required to prevent overweight and obesity.
REFERENCES [ Links ]
2 Steinberger J , Daniels SR, Eckel RH, Hayman L, Lustig RH, McCrindle B, et al.; American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Progress and challenges in metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 2009Feb;119(4):628-47.
3 Lobstein T , Baur L, Uauy R; IASO International Obesity TaskForce. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obes Rev. 2004May;5(s1Suppl 1):4-104. [ Links ]
4 Park MH , Falconer C, Viner RM, Kinra S. The impact of childhood obesity on morbidity and mortality in adulthood: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2012Nov;13(11):985-1000. [ Links ]
5 WHO. Report of the commission on ending childhood obesity. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. [ Links ]
6 Currie C , Hurrelmann K, Settertobulte W, Smith R, Todd J. Health and health behavior among young people. Health Behaviour in Schoolaged Children: a WHO crossnational study (HBSC). Copenhagen: World Health Organization; 2000. [ Links ]
7 Fonseca H , Silva AM, Matos MG, Esteves I, Costa P, Guerra A, et al. Validity of BMI based on selfreported weight and height in adolescents. Acta Paediatr. 2010Jan;99(1):83-8 [ Links ]
8 Cole TJ , Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000May;320(7244):1240-3. [ Links ]
9 Marques A , Gaspar De Matos M. Trends and correlates of overweight and obesity among adolescents from 2002 to 2010: a threecohort study based on a representative sample of Portuguese adolescents. Am J Hum Biol. 2014NovDec;26(6):844-9. [ Links ]
10 Matos M , Simões C, Camacho I, Reis M. Equipa Aventura Social: A saúde dos adolescentes portugueses em tempos de recessão: dados nacionais 2014. Lisboa: Edições FMH; 2015. [ Links ]
11 Marques A , de Mato MG. Trends in prevalence of overweight and obesity: are Portuguese adolescents still increasing weight? Int J Public Health. 2016Jan;61(1):49-56.
12 OECD. Health at a glance 2013: OECD indicators. Paris: OECD Publishing; 2013. [ Links ]
13 Sardinha LB , Santos R, Vale S, Silva AM, Ferreira JP, Raimundo AM, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among Portuguese youth: a study in a representative sample of 1018yearold children and adolescents. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011Jun;6(22):e124-8. [ Links ]
14 Rita A , Cruz de Sousa R, Mendes S, GraçaP. Childhood obesity surveillance initiative. COSI Portugal 2016. Lisboa: Instituto Nacional de Saúde Doutor Ricardo Jorge; 2017. [ Links ]
15 Martínez-Vizcaíno V, Solera Martínez M, Notario Pacheco B, Sánchez López M, García- Prieto JC, Torrijos Niño C, et al. Trends in excess of weight, underweight and adiposity among Spanish children from 2004 to 2010: the Cuenca Study. Public Health Nutr. 2012Dec;15(12):2170-4. [ Links ]
16 Masuet-Aumatell C , Ramon-Torrell JM, Banqué-Navarro M, Dávalos-Gamboa MR, Montaño Rodríguez SL. (Prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents from Cochabamba (Bolivia); a crosssectional study). Nutr Hosp. 2013Nov;28(6):1884-91. [ Links ]
17 Zhang YX , Wang SR. Ruralurban comparison in prevalence of overweight and obesity among adolescents in Shandong, China. Ann Hum Biol. 2013May;40(3):294-7. [ Links ]
18 Rokholm B , Baker JL, SørensenTI. The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999—a review of evidence and perspectives. Obes Rev. 2010Dec;11(12):835-46.
19 Schmidt Morgen C , Rokholm B, Sjöberg Brixval C, Schou Andersen C, Geisler AndersenL, Rasmussen M, et al. Trends in prevalence of overweight and obesity in danish infants, children and adolescents—are we still on a plateau? PLoS One. 2013Jul;8(7):e69860.
20 Olds T , Maher C, Zumin S, Péneau S, Lioret S, Castetbon K, et al. Evidence that the prevalence of childhood overweight is plateauing: data from nine countries. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011Oct;6(56):342-60. [ Links ]
21 Popkin BM , Conde W, Hou N, Monteiro C. Is there a lag globally in overweight trends for children compared with adults?Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006Oct;14(10):1846-53. [ Links ]
22 Sánchez-Cruz JJ , Jiménez-Moleón JJ, Fernández Quesada F, Sánchez-MJ. Prevalence of child and youth obesity in Spain in 2012. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2013May;66(5):371-6.
23 Moreno G , JohnsonShelton D, Boles S. Prevalence and prediction of overweight and obesity among elementary school students. J Sch Health. 2013Mar;83(3):157-63. [ Links ]
24 Hughes AR , Sherriff A, Lawlor DA, Ness AR, Reilly JJ. Incidence of obesity during childhood and adolescence in a large contemporary cohort. Prev Med. 2011May;52(5):300-4. [ Links ]
25 Steinberger J , Jacobs DR, Raatz S, Moran A, Hong CP, Sinaiko AR. Comparison of body fatness measurements by BMI and skinfolds vs dual energy Xray absorptiometry and their relation to cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents. Int J Obes. 2005Nov;29(11):1346-52. [ Links ]
26 Lindsay RS , Hanson RL, Roumain J, Ravussin E, Knowler WC, TataranniPA. Body mass index as a measure of adiposity in children and adolescents: relationship to adiposity by dual energy xray absorptiometry and to cardiovascular risk factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001Sep;86(9):4061-7. [ Links ]
27 Stommel M , Osier N. Temporal changes in bias of body mass index scores based on selfreported height and weight. Int J Obes. 2013Mar;37(3):461-7. [ Links ]
28 WHO. Growing up unequal: gender and socioeconomic differences in young people’s health and wellbeing. Health Behaviour in Schoolaged Children (HBSC) study: international report from the 2013/2014 survey. Copenhagen: World Health Organization; 2016
Received: March 1, 2018. Accepted: September 21, 2018
Statement of Ethics
This research was in accordance with the Ethical Committee of Porto Medical School and the National Data Protection System. All school administrators gave their consent, the legal guardians gave written informed consent, and the students provided assent.
Disclosure Statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Funding Sources
The manuscript received no external financial support.
Author Contributions
Conception and design: Adilson Marques and Margarida Gaspar de Matos.
Data acquisition: Margarida Gaspar de Matos.
Data analysis and interpretation: Adilson Marques, Margarida Gaspar de Matos, Jorge Mota, Maria do Céu Machado, Ana Naia.
Drafting the manuscript: Adilson Marques and Margarida Gaspar de Matos.
Critical revision of the intellectual content: Jorge Mota, Maria do Céu Machado, Ana Naia.
Statistical expertise: Adilson Marques.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Ana Naia.
Study supervision: Margarida Gaspar de Matos.














