Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
GE-Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology
versão impressa ISSN 2341-4545
GE Port J Gastroenterol vol.25 no.6 Lisboa dez. 2018
https://doi.org/10.1159/000487035
ENDOSCOPIC SNAPSHOT
Challenging Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent Removal after Successful Drainage of a Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Remoção desafiante de prótese metálica de aposição luminal após drenagem com sucesso de pseudoquisto pancreático
Athanasios D. Sioulasa, Konstantina Papadakia Dimitrios Schizasb, Ilias Scotiniotisa
aDepartment of Gastroenterology, Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece; b1st Department of Surgery, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Laikon Hospital, Athens, Greece
* Corresponding author.
Keywords: Complications, Pancreas, Pseudocyst drainage
Palavras-Chave: Complicações, Pâncreas, Drenagem de pseudoquisto
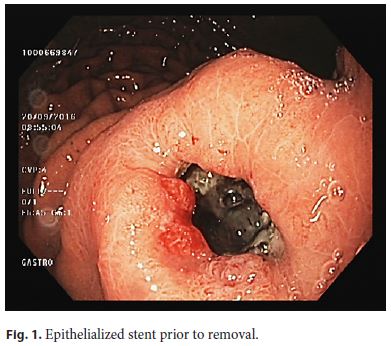
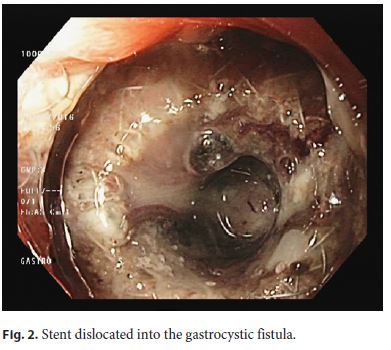
A 45-year-old man with a symptomatic 14-cm-sized pancreatic body pseudocyst following alcohol-induced acute pancreatitis 19 months earlier was treated with placement of a lumen-apposing metal stent. The stent (Hot Axios, Boston Scientific Corporation, Marlborough, MA, USA) had a length of 1 cm and a diameter of 10 mm and was inserted under endosonographic guidance. The patient experienced immediate relief of symptoms and imaging studies confirmed the complete resolution of the pseudocyst. Endoscopy 11 weeks later revealed epithelial overgrowth of its gastric flange (Fig. 1), though the stent was visible within the gastrocystic fistula (Fig. 2). Stent removal by means of a rat-tooth forceps was performed, but necessitated significant maneuvering in order the gastric flange to be released. No procedure-related complications were encountered. Thus, the recommended 8-week period for lumen-apposing stent removal should not be significantly exceeded, to prevent a buried stent syndrome secondary to epithelial overgrowth at its gastric end [1–3].
References
1 Bang JY, Hasan M, Navaneethan U, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S: Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) for pancreatic fluid collection (PFC) drainage: may not be business as usual. Gut 2017;66:2054–2056. [ Links ]
2 Rodrigues-Pinto E, Grimm IS, Baron TH: Removal of buried gastroduodenal stents after drainage of pancreatic fluid collections: Silence of the LAMS (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2016;83:853–854. [ Links ]
3 Patil R, Ona MA, Papafragkakis C, Anand S, Duddempudi S: Endoscopic ultrasoundguided placement of AXIOS stent for drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. Ann Gastroenterol 2016;29:168–173. [ Links ]
Disclosure Statement
All authors confirm that there is no conflict regarding this publication.
* Corresponding author.
Dr. Athanasios D. Sioulas
Department of Gastroenterology, Hygeia Hospital
4 Erythrou Stavrou Street and Kifissias Avenue
GR–15123 Athens (Greece)
E-Mail athsioulas@yahoo.gr
Received: December 11, 2017; Accepted after revision: January 9, 2018














