Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Angiologia e Cirurgia Vascular
versão impressa ISSN 1646-706X
Angiol Cir Vasc vol.13 no.1 Lisboa mar. 2017
CASO CLÍNICO
Tratamento endovascular de um aneurisma justarenal com a técnica “chimney”
Endovascular treatment of a juxtarenal aortic aneurysm with the chimney technique
Ryan Gouveiae Melo2,3, Ruy Fernandese Fernandes1,2,3, Luís M. Pedro1,2,3, Luís Silvestre2,3, Gonçalo Queiroz e Sousa2, Pedro Garrido2, J. Fernandes e Fernandes1,2,3
1 Centro Académico de Medicina de Lisboa.
2Serviço de Angiologia e Cirurgia Vascular, Hospital Santa Maria (CHLN), Lisboa.
3Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de Lisboa.
RESUMO
O tratamento endovascular dos aneurismas justarenais é um desafio complexo para o cirurgião vascular. Os autores apre sentam um caso de um doente de 83 anos com um aneurisma juxtarenal de grandes dimensões tratado com uma abordagem endovascular aórtica com recurso a “chimneys” para a artéria renal esquerda e artéria mesentérica superior. Nos aneurismas juxtarenais o recurso a endopróteses fenestradas tem sido reconhecida como a opção endovascular preferível, no entanto, em casos em que o risco de rotura é considerado elevado para aguardar pela produção de um dispositivo e/ou a anatomia é desfa vorável o recurso ao tratamento endovascular com “chimneys” é uma opção viável e prontamente disponível. O caso apresen tado é um exemplo da aplicabilidade deste tratamento, com resultado positivo conforme demostrado.
Palavraschave: CHEVAR; endoprótese Chimney; endoprótese Snorkel; Aneurisma juxtarenal; Reparação endovascular complexa; Caso clínico
ABSTRACT
Endovascular treatment of juxtarenal aortic aneurysms is a complex challenge to the vascular surgeon. We present a case of an 83 year old man with a large juxtarenal aneurysm treated with an endovascular approach with chimneys to the left renal artery and superior mesenteric artery. enestrated aortic endovascular repair has been considered the preferred endo vascular approach in juxtarenal aneurysms, however when the risk of rupture is considered high to wait for a manufactu red device and/or when the anatomy is not suitable for a fenestrated repair, chimney endovascular repair is a viable and promptly available option. This case report is an example of the applicability of this treatment with a positive shortterm outcome as shown here.
Keywords: CHEVAR; Chimney grafts; Snorkel grafts; EVAR; Juxtarenal aortic aneurysm; complex endovascular repair; Case Report
INTRODUCTION / INTRODUÇÃO:
Juxtarenal aortic aneurysms (JRAA) represent around 15% of all abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA).1 Endovascular repair of AAAs has become a fast growing trend in vascular surgery. However, as the anatomy of a JRAA makes infrare nal sealing of an endovascular graft not feasible, JRAAs still represent a complex challenge to the vascular surgeon.
Surgical options may include open aortic surgery with suprarenal clamping, hybrid open debraching/endovascu lar surgery, fenestrated endovascular aortic repair (FEVAR) and endovascular repair with parallel stentgrafts. The latter group includes “snorkel” or “chimney” (CHEVAR), the “periscope” and “sandwich” techniques.1,2
The endovascular approach is particularly advantageous in patients with high surgical risk, like the elderly and those with multiple comorbidities.
We report a case of an 83 year old man, with an 11 cm JRAA treated successfully by CHEVAR.
CASE REPORT / CASO CLÍNICO:
An 83 year old man was referred to our Outpatient Clinic by his regular doctor after a 10cm aortic aneurysm was found in a routine abdominal ultrasound.
The patient was asymptomatic and had a history of hyper tension, hypercholesterolemia, chronic heart failure (stage II of the NYHA), chronic kidney disease with a single func tioning left kidney (base creatinine: 1.83mg/dl and GFR: 33.2ml/min/1.73m2) and atrial fibrillation. He was submit ted to a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) with greater saphenous vein and an aortic valve replacement with a mechanical valve in 2013. His regular medication included warfarine, spirinolactone, furosemide, bisoprolol, estazo lam and sublingual nitroglycerin.
The patient presented with an abdominal pulsatile and expandable mass, with a positive DeBakey sign, with good and overall symmetrical arterial pulses and no other rele vant findings on physical examination. The patient was admitted straight to our Vascular Surgery ward for prompt workup and treatment.
A thoracic, abdominal and pelvic CT angiography (CTA) showed a JRAA with an 11 cm diameter starting at the level of the left renal artery (LRA) extending until the iliac bifur cation, a LRA stenosis, occlusion of the right renal artery and celiac artery stenosis. The aneurysm had a hourglass and angulated architecture with an infrarenal sharp curva ture (Figure 1).
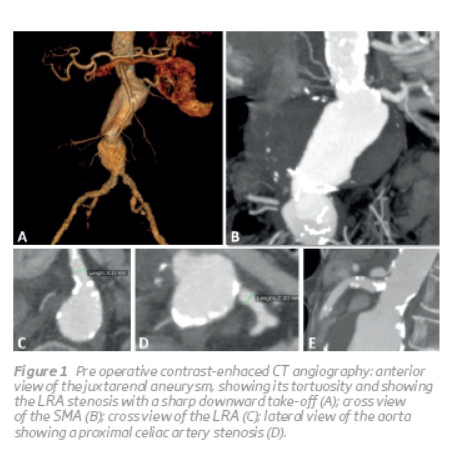
The remaining preoperative evaluation showed a good pulmonary reserve, with no other relevant findings.
Since the patient had a high surgical risk, the discussion remai ned between which endovascular approach to follow, after a board discussion about the case, a decision to proceed to an endovascular approach using the “chimney” technique was made due to the anatomy and risk of rupture of the aneurysm. The patient was scheduled for elective surgery and a CHEVAR with “chimneys” grafts (CG) to the LRA and superior mesen teric artery (SMA) and celiac artery angioplasty with stent for concomitant occlusive disease were planned.
The procedure was performed in an angiographic suite, with the patient under general anesthesia and systemic hepari nization (as needed for target ACT =200). Surgical exposure of the left and right axillary artery (LAA, RAA) and bilateral common femoral artery (LCFA, RCFA) were obtained. At the femoral arteries, purse string sutures were created to allow early declamping of the lower limbs circulation. Access of the celiac artery and SMA were planned through the right axilar artery and the LRA through the left axilar artery.
The first step of the procedure was catheterization of the celiac artery and treatment with angioplasty and placement of a balloonexpandable stent (Hippocampus® 6x20mm Medtronic®, Minneapolis, Minn). Afterwards sequential catheterization and positioning of a selfexpanding cove red stent (Viabahn® Gore®, Flagstaff, AZ) for the CG's was performed in the SMA and LRA respectively. Due to difficult catheterization of the LRA and inability to progress a sheath over a stiff guidewire (Rosen®, COOK Medical®, Bloomington, Ind) a short covered balloonexpandable stent (Advanta V12® 6x22mm, Atrium Medical Corporation®, Hudson, NH) was deployed at the ostium, facilitating access to the LRA and parking of the CG.
Through the RCFA a Zenith graft (COOK Medical®, Bloomington, Ind; main body 32x128mm;) was positioned in the abdominal aorta, aligned with the lower border of the celiac artery. Then the CG were sequentially deployed (SMA and LRA). During the release Viabahn® stentgraft in the SMA, the sheath was not sufficiently pulled back which caused the Viabahn® to be partiallyopenedandproximallystuckinsideit. Withmobilization of the sheath, the stent graft was displaced from the SMA and both were pulled togetherto the RAA, withoutlosing the guide wire placed at the SMA. The Viabahn® was then partially exter nalized and clamped, allowing access to be regained to the SMA with introduction of a new sheath (Figure 2F) and continue the procedure. A new Viabahn® (8x100mm) was deployed at the SMA and relined with a selfexpanding stent (S.M.A.R.T.® flex 8x60mm, Cordis®, Fremont, CA) to prevent compression of the CG by the aortic endograft. Similar steps were repeated for the LRA CG (Viabahn® 6x100mm and relining stent(S.M.A.R.T.® flex 7x60mm, Cordis®, Fremont, CA)). A selective angiogram was performed aftercompletion ofeach CG and confirmed adequate positioning and flow on the target vessel(Figure 2 A, B, C).
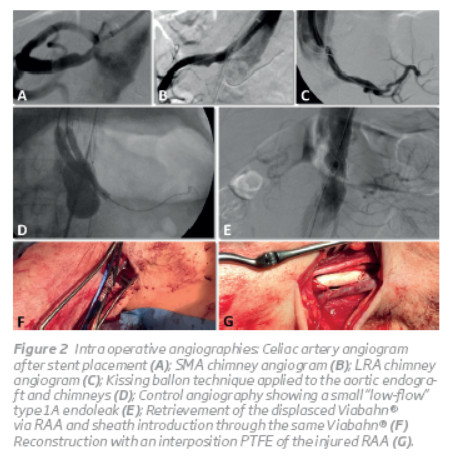
The bifurcated graft was then deployed at the same time as the CGs were proximally pulled with inflated balloons to achieve a better alignment between the CG's and the aortic endograft. After deployment of the bifurcated aortic graft, a kissing balloon technique was applied by simulta neous chimney and aortic graft balloon inflation and pulling in order to seal the “gutters” correctly (Figure 2D). Finally the iliac limbs were deployed (left limb: Zenith SpiralZ 1674mm; right limb: Zenith SpiralZ 2074mm, COOK Medi cal®, Bloomington, Ind).
The completion angiogram showed correct exclusion of the whole aneurysm with patency of both CG, and hypogastric arteries. However, the celiac artery stent had been dislodged and parked inside the aortic maingraftand a smalland lowflow type IA endoleak was observed next to the renal chimney “gutter” (Figure 2E), whichwas managed conservatively.
Complete removal of the externalized Viabahn® at RAA was not possible due to significant resistance on pullback, so a surgical reconstruction of the artery was performed with partial resection of the Viabahn® and interposition of a 6 mm PTFE graft, englobing the remaining Viabahn® on the proximal anastomosis (Figure 2G).
The post operative recovery was complicated by an acute renal failure (AKIN III), which was medically treated without need of dialysis, with recovery of preoperative renal func tion, and by a urinary tract infection by Proteus mirabilis which was treated with IV antibiotics.
A control CTA performed at 12 days postoperatively showed correct aneurysm exclusion, CG patency and no endoleaks (Figure 3). The stainless steel stent initially placed in the celiac artery remained in the same position as obser ved inside the main aortic graft.
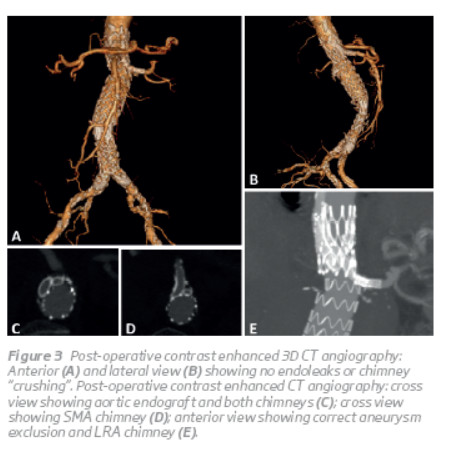
The patient was discharged on the 18th day after surgery, clini cally well, andis currentlyaliveandwell, 4 months after surgery.
DISCUSSION / COMENTÁRIOS:
Open aortic surgery still remains the gold standard for the treatment of JRAAs.1 However, patients with a higher surgi cal risk, may benefit from an endovascular treatment option. FEVAR has gained acceptance throughout Europe and the United States and is now considered an alternative option, especially for unfit patients.1, 3 Recently, selected highvo lume centers have published their experience of FEVAR as the firstline treatment for all patients with a JRAA reporting excellent high technical success, low operative mortality rates and good midterm durability.3 Chimney and snorkel techniques were initially described by Greenberg et al as bailout procedure when aortic branches were covered by an endovascular aortic graft during endovascular aortic repairs4, but have also been described as an alternative option for JRAA1,2,5 , specially in centers where FEVAR was notavailable.5 To date, no randomised trials comparing these different treatment modalities have been published. A selection bias is commonly recognized in the available literature, with younger and healthier patients treated by an open approach and endovascular techniques reserved for older and sicker patients.1 Katsagyris et al1 conducted a review of the literature reporting FEVAR, CHEVAR and open surgical treatment of JRAA and showed similar operative mortality between the approaches and favourable comparison for FEVAR in terms of morbidity. CHEVAR was associated with higher incidences of endoleak IA and ischemic stroke rates and the authors concluded that CHEVAR should be reser ved for acute patients and elective patients who are poor candidates for open surgery or FEVAR.1
Although offthe shelf fenestrated grafts have been docu mented, these are notwidely accessible,2 and usually FEVAR implies a custommade fenestrated graft to be manufactu red, which take at least 4 to 6 weeks.1,2 Anatomic restric tions also exist for FEVAR: heavily angulated aneurysms (angulations over 45º) and sharp lower renal and visceral artery takeoffs are considered contraindications.2
CHEVAR usually implies an axillary approach, which increa ses the risk of neurological events, such as strokes1, in patients with highly calcified and tortuous aortic arch and supraaortic vessels.1,2,6 Patients with CABG involving the internal mammary artery (IMA) should be conside red contraindicated for an axillary access, as advancing a sheath through the subclavian artery may temporary occlu de the IMA, leading to myocardial ischaemia.6 However, in such cases which may preclude antegrade catheterization, Lachat et al described the “Lift Technique” which is feasible and may be used appropriately in these cases.6,7
As CHEVAR is a relatively recent techique,3 with a low number of cases reported,1 and no specifically grafts and materials designed for it, some aspects of the technique are still widely controversial.2,5,8
A higher incidence of type I endoleaks has been documen ted in patients treated with CHEVAR.1,2 These endoleaks tend to develop in the unavoidable “gutters” which are crea ted between the CG, the main aortic graft and the aortic wall itself. It has been postulated that better sealing is obtained with an overlap of the CG against the main aortic graft of at least 20mm, a graft oversizing of 20–30% and simulta neous inflation and “pulling” of the grafts in order to align and seal the “gutters” correctly.2,5 However, there is still some controversy regardind the use of either balloon or selfexpandable CGs, which aortic graft and what sequence of deployment to use.2,5,7
In our center open surgery is considered the firstline treat ment for JRAA in patients considered fit for surgery and FEVAR the first option in high–risk patients. Our patient was an 83 year old man, with multiple comorbidities and considered unfit for open surgery. As the aneurysm had a diameter of 11cm, we believed that the risk of rupture was high and precluded waiting for the manufacture of a custommade fenestrated graft. Anatomical constraints also existed, mainly a significant angulation between the pararenal aorta and the aortic aneurism and a downward takeoff and ostial stenosis of the LRA. The patient's aortic arch and supraaortic vessels were also favourable for an axillary access.
The complications that occurred in the reported procedure show that CHEVAR is a technical demanding and complex procedure. Mobilization of a chimneygraft during deploy ment was undoubtedly a technical error that was also favoured by the low visibility of an expanded Viabahn® in full lateral view and emphasises the need of high quality image systems to perform safely advanced aortic proce dures. Careful planning and multiple bailout options, inclu ding a large stock of inhouse stents and catheters, are also needed to obtain a high technical success.
CONCLUSION / CONCLUSÃO:
CHEVAR seems to be an appropriate and valid therapeutic option for the treatment of patients with JRAA who are poor candidates for open surgery and FEVAR.1,5,9 Patients who are unfit for open surgery, who have a high risk of aneurysm rupture seem to be the best candidates.1,2,5,7 Our patient fit this description and was treated successfully with CHEVAR, with favourable outcome at 4 months of followup.
CONSENT/ CONSENTIMENTO INFORMADO:
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication ofthis case reportand accompanying images.
AKNOWLEGEMENTS/ AGRADECIMENTOS:
All of the authors were responsible for the development and revision of the case report.
FUNDING/ FINANCIAMENTO:
There was no financial or other support from industry.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT/ CONFLITO DE INTERESSES:
None
REFERENCES/ BIBLIOGRAFIA:
Katsargyris A, Topel I, Oikonomou K, et al. Comparison of Outcomes With Open, Fenestrated, and Chimney Graft Repair of Juxtarenal Aneurysms: Are We Ready for a Paradigm Shift? J Endovasc Ther. 2013;20:159–169. [ Links ]
Patel R, Katsargyris A, Verhoeven E, et al. Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair with Chimney and Snorkel Grafts: Indications, Techniques and Results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013. 36:14431451. [ Links ]
*Autor para correspondência
Correio eletrónico: ryan@campus.ul.pt (R. Melo).
Recebido a 07 de junho de 2016;
Aceite a 11 de dezembro de 2016.














