Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Angiologia e Cirurgia Vascular
Print version ISSN 1646-706X
Angiol Cir Vasc vol.12 no.3 Lisboa Sept. 2016
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ancv.2016.03.003
CASE REPORT
Aortoesophageal fistula in a patient with carcinoma of the esophagus - Case report
Fístula aorto-esofágica em doente com neoplasia do esófago - Caso clínico
Gonçalo Queiroz de Sousaa, *, Ruy Fernandes e Fernandesa, Luís Mendes Pedroa, Pedro Garridoa, Luís Silvestrea, Paulo Costab, José Fernandes e Fernandes a
a Clínica Universitária de Cirurgia Vascular, Hospital de Santa Maria Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de Lisboa, Centro Académico de Medicina de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal
b Clínica Universitária de Cirurgia 1, Hospital de Santa Maria Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
ABSTRACT
Primary aortoesophgeal fistulas (AEF) are a rare but life-threatening condition because of substantial hemorrhage, requiring fast treatment to ensure patient survival. We report a case of a 69-year-old male with diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus who suffered an episode of hematemesis and hemorrhagic shock. Gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy revealed an ulcerated lesion with pulsatile hemorrhage. CT-scan confirmed the diagnosis of AEF. A stent-graft was placed in the descending aorta to control bleeding, and 2 days later an esophageal stent was deployed to reduce risk of aortic graft infection. The patient was discharged 13 days after admission and had no other episode of GI bleeding in a 6-month follow-up period. TEVAR may be used as a palliative or bridge treatment of AEF.
Keywords: Aortoesophageal fistula; Aorta; Endovascular stentgraft; Esophageal stent; Upper gastrointestinal bleeding
RESUMO
As fistulas aorto-esofágicas (FAE) primárias são raras mas com elevada mortalidadeaorto-esofágica; devido à hemorragia digestiva substancial, necessitando intervenção rápida para garantir aAorta; sobrevivência do doente. Os autores apresentam um caso dum homem de 69 anos com carcinomaEndoprótese aórtica; esofágico que teve episódio de hematemeses e choque hemorrágico. A endoscopia digestiva altaStent esofágico; mostrou lesão ulcerada com hemorragia pulsátil, a angioTC confirmou o diagnóstico de FAE. FoiHemorragia digestiva colocada endoprótese na aorta descendente para controlo da hemorragia; dois dias depoisalta foi colocado stent esofágico para reduzir risco de infecção da endoprótese. O doente teve alta ao décimo terceiro dia, e não foi reportada hemorragia digestiva nos seis meses de seguimento. Este caso mostra como o TEVAR pode ser usado como tratamento paliativo ou temporário duma FAE.
Palavras-chave: Fístula aorto-esofágica; Aorta; Endoprótese aórtica; esofágico; Hemorragia digestiva alta
Introduction
A primary aortoesophageal fistula (AEF) is a communication between the aorta and the esophagus, without previous surgery. Being a rare entity, the most frequent causes are thoracic aortic aneurysm, foreign body ingestion and esophageal malignancy, being the thoracic aortic aneurysm by far the most common cause.1 It is a life-threatening condition due to massive upper gastrointestinal bleeding, so prompt treatment is mandatory for patient survival.
Here we report a case of primary AEF treated successfully with a stent-graft.
Clinical case
A 63-year-old caucasian male, with coronary heart disease (NSTEMI in 2007) and known diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus since early 2014, which had been staged T3N+M0 in June 2014, underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy (two cycles of cisplatin + 5-fluorouracil) and radiotherapy (50.4 Gy) between July and September and had surgery of the esophagus scheduled for mid-October.
However, in early October he was admitted to the Emergency Department with fever (39.2 ◦C) plus vomits and melena for 3 days. He presented with hypotension (96/59 mmHg), and had a painless abdomen on observation. Lab results revealed a hemoglobin of 10.5 g/dL, platelets of 31,200/L and reactive C protein of 15.2 mg/dL.
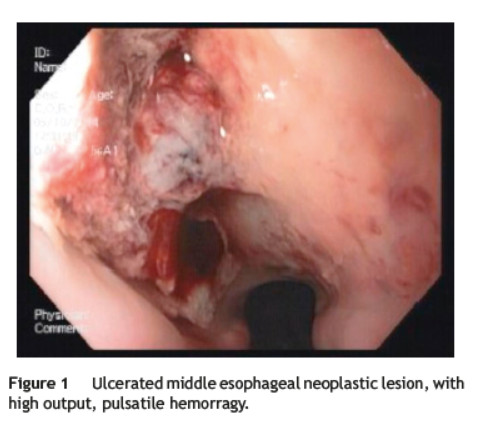
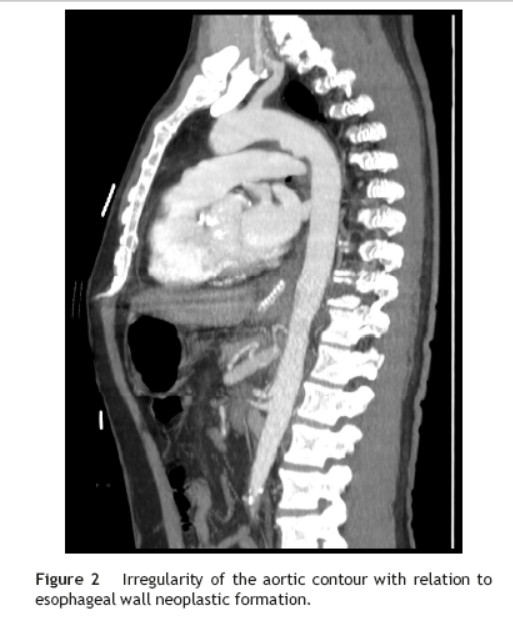
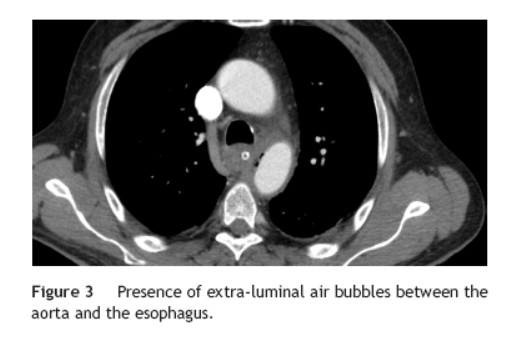
He was transferred to a Medicine Ward and on the next day suddenly lost conscience after an episode of hematemesis. His hemoglobin fell to 6.8 g/dL. After fluid resuscitation, the patient recovered from the hemorrhagic shock. An upper gastrointestinal endoscopy showed an ulcerated middle esophagial neoplastic lesion, with a high output, pulsatile hemorragy, with high probability of AEF (Fig. 1). A CT angiogram was performed, and identified the presence of air bubbles between the aorta and the esophagus, with irregularity of the aortic contour in this location, with extravasion of contrast in the arterial phase of the exam, suggestive of AEF (Figs. 2 and 3).
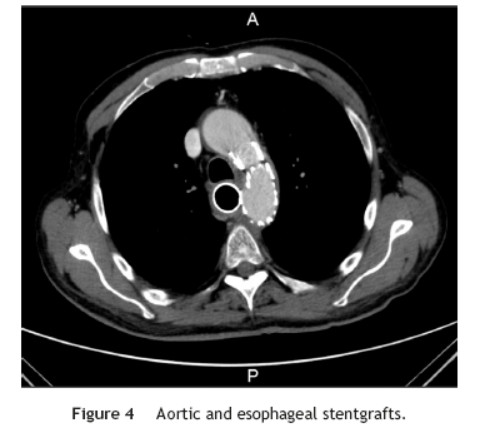
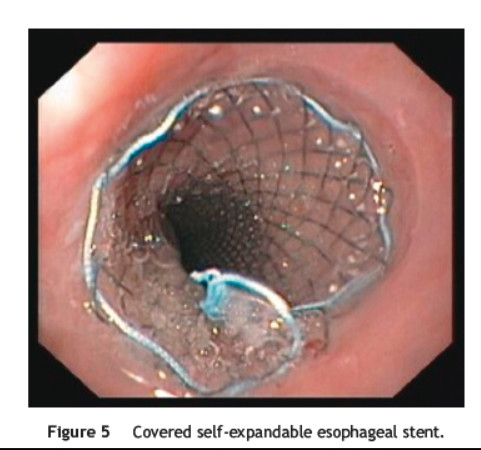
After admission in the ICU, and following a multidisciplinary discussion of the case, endovascular treatment was performed with a Cook® Zenith TX2 30 mm × 140 mm stent graft deployed in the descending aorta, beyond the origin of the left subclavian artery (Fig. 4). Two days later a covered self-expandable esophageal stent was placed with the intent of reducing the risk of aortic stent graft infection (Fig. 5). Both procedures had no short-term complications. The patient had no more episodes of gastrointestinal bleeding, kept hemodynamic stability, and was discharged 13 days after admission in the Hospital Emergency Department.
Since then, the patient kept follow-up in outpatient clinic, is doing prophylactic therapy with amoxicillin clavulanate, and has had several re-admissions in Medicine Ward with difficult-to-control pain, dysphagia for solid food but not for liquids, and progressive weight loss. There were no more episodes of gastrointestinal bleeding reported in a 6month follow-up period.
Discussion
This case reports a life-threatening condition that requires fast decisions in order to save a patient's life, while trying to offer a lasting solution for the esophageal and the aortic lesions.
In 1991, Hollander and Quick published a review of the available literature regarding AEF, where esophageal cancer was the third leading cause of AEF, and at that time rapid surgical intervention was recommended as the only chance for patient survival, since all the cases which had been managed in a conservative way had died of exsanguination.1
After the introduction of endovascular aortic repair,2 a new alternative for the treatment of AEF has been proposed.
In these patients there is another challenge, infection. One must consider that infection is, by principle, present in this group of patients3,4 which makes open surgery and debridement of infected tissues the treatment of choice for these patients. The commonly used technique for open repair of AEF requires left thoracotomy and aortic replacement or even extra-anatomic bypass in cases of serious infection.5 However, open surgery is related with high-mortality rate in this group of patients,1 although exact mortality rates are not available in literature due to the low number of cases of AEF.
This is why endovascular exclusion of thoracic aortic fistulas with TEVAR may definitely have a role, especially in the rapid control of hemorrhage in often physically and physiologically fragile patients.6
In the literature there are only small series or case reports published describing the use of TEVAR in the management of AEF, but this technique should be considered as a palliative treatment,7 or a ‘‘bridge'' until the patient is healthy enough to endure open surgery,3,7 with broad-spectrum antibiotherapy to control infection. Allen4 considers that TEVAR ‘‘should be used only for specific indications, such as infection with low-virulence organisms, absence of gross purulence, and high operative risk''.
Moreover, after the diagnosis of the AEF this tumor is now a T4b (unresectable), and staged IIIc, which according to the NCCN guidelines is candidate for chemotherapy if the patient tolerates it, or only palliative management.9
In our patient, and in order to reduce the contact of the endograft with the septic environment of the esophagus as well as providing sealing of the fistula on the esophageal side, a self-expandable covered esophageal stent was used. One report8 describes the use of an esophageal stent as the first means to tamponade and control hemorrhage from AEF, followed by TEVAR. In this report, the patient died 2 months later of disseminated malignancy.
Conclusion
Endovascular management of urgent cases of AEF with TEVAR is a feasible technique, and may have a role in a specific group of patients, especially those that do not have conditions for open surgery or are in terminal phase of malignant disease.
The use of concomitant esophageal stenting may have the potential of reducing the infection of the aortic stent-graft, but this needs to be supported by other studies.
However, there is only a low number of published cases, and we have limited time of follow-up, so more evidence is necessary to evaluate long-term outcomes of this treatment option for AEF.
References
Hollander JE, Quick G. Aortoesophageal fistula: a comprehensive review of the literature. Am J Med. 1991;91:279-87. [ Links ]
Parodi JC, Criado FJ, Barone HD, et al. Endoluminal aortic aneurysm repair using a balloon-expandable stent-graft device: a progress report. Ann Vasc Surg. 1994;8:523-9. [ Links ]
González-Fajardo JA, Gutierréz V, Martin-Pedrosa M, et al. Endovascular repair in the presence of aortic infection. Ann Vasc Surg. 2005;19:94-8. [ Links ]
Allen RC, Sebastian MG. The role of endovascular techniques in aortoesophageal fistula repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2001;8:602-3. [ Links ]
Topel I, Stehr A, Steinbauer MG, et al. Surgical strategy in aortoesophageal fistulae: endovascular stentgrafts and in situ repair of the aorta with cryopreserved homografts. Ann Surg. 2007;246:853-9. [ Links ]
Jonker FHW, Heijmen R, Trimarchi S, et al. Acute management of aortobronchial and aortoesophageal fistulas using thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J Vasc Surg. 2009;50:999-1004, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2009.04.043. [ Links ]
Flores J, Shiya N, Kunihara T, et al. Aortoesophageal fistula: alternatives of treatment case report and literature review. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;10:241-6. [ Links ]
Ghosh SK, Rahman FZ, Bown S, et al. Survival following treatment of aortoesophageal fistula with dual esophageal and aortic intervention. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2011;5:40-4. [ Links ]
Ajani JA, Barthel JS, Bentrem DJ, et al. Esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancers. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2011;9:830-87. [ Links ]
Ethical diclosures
Protection of human and animal subjects. The authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this investigation.
Confidentiality of data. The authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consent. The authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
E-mail address: queiroz.sousa@gmail.com (G. Queiroz de Sousa).
Received 4 June 2015;
Accepted 13 March 2016
Available online 26 April 2016














