Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Acta Obstétrica e Ginecológica Portuguesa
versão impressa ISSN 1646-5830
Acta Obstet Ginecol Port vol.12 no.2 Coimbra jun. 2018
CASE REPORT/CASO CLÍNICO
Congenital chylothorax - a case report
Quilotoráx congénito - relato de um caso clínico raro
Bruna Ambrosio*, Joaquim Fonseca**, Ana Paula Ferreira**
Hospital Prof. Doutor Fernando Fonseca
*Interna da Especialidade de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia
**Assistente Hospitalar Graduado de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia
Endereço para correspondência | Dirección para correspondencia | Correspondence
ABSTRACT
Congenital chylotorax is the most common form of pleural effusion in the prenatal period, although it is rare. The etiology of this condition isn't clear, but it is thought to be related to congenital malformations of the lymphatic system. The overall mortality rate is 25%-50%, but it could be higher. Congenital chylotorax complicated with hydrops in a premature newborn is an uncommon and serious clinical problem. We report a case of a congenital bilateral chylothorax with early and severe prenatal presentation. The outcome was bad, with neonatal death, despite all the efforts in his management.
Keywords: Pleural effusion; Congenital chylothorax; Hydrops; Thoracocentesis.
Introduction
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity, and be caused by chylothorax, hemothorax, empyema, hydrothorax, or leakage of central-line fluid. Congenital chylotorax is the most common form of pleural effusion in the prenatal period1, although it is a very rare condition2. It is usually unilateral (> 90% of the cases) and its occurrence is estimated in approximately 1 in 10000-15000 pregnancies2, more frequently in males, in a 2:1 proportion3, with an overall mortality rate of 25% to 50%1,4. Chylothorax is defined as the accumulation of lymph in the pleural cavity and may be classified as congenital or acquired. The etiology of congenital chylotorax is not clear, but it is thought to be related with congenital malformations of the lymphatic system, leading the leakage of lymphatic fluid from the thoracic duct or one of its main tributaries. Related conditions included chromosomal anomalies (Trisomy 21 and Noonan syndrome), neck cystic hygroma, lung sequestration, fetal junctional rhythm and placental chorioangioma. After the diagnosis of pleural effusion, it is essential to perform a detailed investigation to exclude other conditions and secondary pleural effusion2. Primary pleural effusion is a diagnosis of exclusion that can be established only after ruling out congenital infections, immune hydrops, fetal anemia and chromosomal abnormalities2,3. In order to consider congenital chylothorax as the cause of primary pleural effusion, pleural fluid must be analyzed by thoracocentesis. Diagnosis of congenital chylothorax is made when there is a white cell count greater than 1000/ml, with a lymphocyte fraction above 70%1,3. The natural history is variable. The effusion may resolve spontaneously, remain stable or progress to hydrops with fetal or neonatal demise. The coexistence of hydrops, bilateral occurrence, pulmonary hypoplasia, preterm labor, absence of pre-natal treatment and accompanying genetic syndrome are associated with poor neonatal outcomes1,2,6. Pre-natal treatment options include repeated thoracocentesis, pleuro-amniotic shunting and fetal pleurodesis. There are no randomized trials comparing these different options and the optimal antenatal management is still controversial2. Despite this, the majority of authors conclude that when chylothorax is diagnosed before 34 weeks, prenatal therapy allows improved postnatal outcomes2,6-9.
Case report
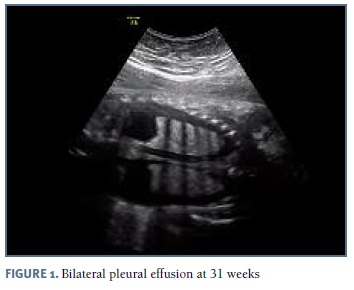
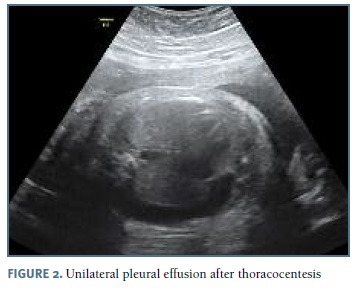
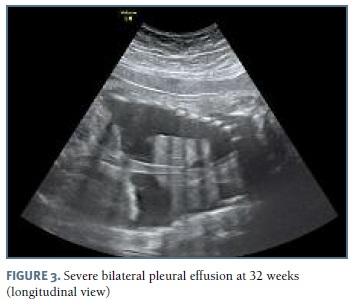
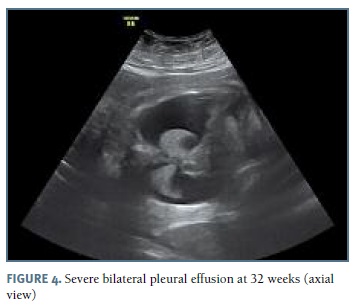
The authors present a case of a 33-year-old pregnant woman followed in our obstetric department since 27 weeks of gestation, after the diagnosis of bilateral pleural effusion. The patient had no relevant medical history and no children, with two previous 1st trimester fetal losses. Her blood type was O Rh positive. Her pregnancy surveillance was normal, with unremarkable ultrasounds at 12 and 22 weeks. At 26 weeks gestation, pleural effusion was diagnosed by routine scan and the patient was referred to our hospital. At 27 weeks, after confirmation of an isolated pleural effusion, the parents were informed about the prognosis and diagnostic/therapeutic options and refused any invasive procedure. Fetal echocardiography at 28 weeks was normal. The 29 weeks scan revealed a fetus in the 75th percentile with normal amniotic fluid index, no signs of fetal anemia and mild pleural effusion. Lab results for viral infections (TORCH group, parvovirus B19 and VDRL) were negative. At this time she started fetal lung maturation with four administrations of intramuscular dexamethasone (6 mg each). Two weeks later, as the pleural effusion increased significantly (Figure 1), the parents agreed to perform an amniocentesis and thoracocentesis; 60 ml of yellow-colored fluid were drained from the left side. Fetal karyotype was normal (46, XY) and the cytological analysis of the fluid demonstrated a white cell count greater than 1000/μl, with 99% of lymphocytes, suggestive of congenital chylothorax. Control ultrasound at 32 weeks (1 week after the procedure) reveled a large bilateral pleural effusion (Figures 3 and 4), polyhydramnios and signs of hydrops. Insertion of a double-pigtailed pleuro-amniotic shunt was attempted, without success, followed by a repeated thoracocentesis in the same day, which was unsuccessful. The patient was then transferred to the obstetrics emergency department for surveillance and an emergency cesarean section was performed some hours later for suspected fetal distress. A male newborn weighing 2325g was delivered, but, despite all efforts (endotracheal intubation, thoracocentesis, cardiac massage, adrenaline, volume expansion) the Apgar score was 1-0-0 at 1st, 5th and 10th minutes, with neonatal death declared 30 minutes after birth.
Discussion
The congenital chylothorax case presented had an early and severe presentation and the parents were very reluctant to perform invasive procedures. Prolonged severe fetal pleural effusion can compromise normal lung maturation and progress to fetal hydrops, ultimately resulting in premature birth and pulmonary hypoplasia, with a high rate of intrauterine death and perinatal mortality. Despite the effort in antenatal treatment with thoracocentesis, the fetus developed hydrops and the reanimation after delivery was unsuccessful. The majority of authors recognize the advantages of prenatal diagnosis, ultrasound monitoring and prompt therapeutic interventions in these cases. Prenatal therapy is a prognostic modifier, preventing the most severe forms of hydrops and pulmonary hypoplasia. An overall mortality up to 50% has been reported in some series, with poor prognosis associated with: diagnosis before 32 weeks, delivery before 35 weeks and coexistence of hydrops4. When poor prognostic factors are present, some authors report mortality rates higher than 90%. Our case combined all these poor prognostic factors and, despite the efforts, ended with the newborn death.
REFERENCES
1. Brito T, Oliveira C, Sousa L, Barbosa A, Pinho O, Mesquita M, Pinto R, Inocêncio A, Valente F. Congenital chylothorax: a case report. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 21:70-71. [ Links ]
2. Yinon Y, Kelly E, Ryan G. Fetal pleural effusions. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2008; 22: 77-96. [ Links ]
3. Rocha G, Guerra P, Azevedo I, Guimarães H. Chylothorax in the fetus and the neonate - guidelines for treatment. Rev Port Pneumol 2007; 13: 377-381. [ Links ]
4. Dubin PJ, King IN, Gallagher PG. Congenital chylothorax. Curr Opin Pediatr 2000; 12: 505-509. [ Links ]
5. Klam S, Bigras JL, Hudon L. Predicting outcome in primary fetal hydrothorax. Fetal Diagn Ther 2005; 20: 366-370. [ Links ]
6. Rustico MA, Lanna M, Coviello D, Smoleniec J, Nicolini U. Fetal pleural effusion. Prenat Diagn 2007; 27: 793-799. [ Links ]
7. Nicolaides KH, Azar GB. Thoraco-amniotic shunting. Fetal Diagn Ther 1990; 5: 153-164. [ Links ]
8. Lee CJ, Tsao PN, Chen CY, Hsieh WS, Liou JY, Chou HC. Prenatal Therapy Improves the Survival of Premature Infants with Congenital Chylothorax. Pediatr Neonatol 2016; 57: 127-132. [ Links ]
9. Deurloo KL, Devlieger R, Lopriore E, Klumper FJ, Oepkes D. Isolated fetal hydrothorax with hydrops: a systematic review of prenatal treatment options. Prenat Diagn 2007; 27: 893-899. [ Links ]
Endereço para correspondência | Dirección para correspondencia | Correspondence
Bruna Ambrosio
Portugal
E-Mail: brambrosio@hotmail.com
Recebido em: 20/06/2017
Aceite para publicação: 09/12/2017